- Is a Wash & Cure Station Worth It? Creality UW-03 Review - April 29, 2024
- Z Seam | How to Hide & Avoid | Cura & PrusaSlicer - April 20, 2024
- Qidi Tech Q1 Pro – Best Orca Slicer Settings & Profile - April 9, 2024
Disclosure: Links marked with * are Affiliate Links. I earn from qualifying purchases if you decide to make a purchase through these links – at no additional cost for you!
Would you like to get started with 3D printing and are wondering how? We answer the most important initial questions: from choosing a printer and processing different materials to completing your first printing project.
In this article, you’ll find all the information you need in a compact and easy-to-understand format.
Table of Contents:
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 3D Printing Basics
- 3 Choosing the Right 3D Printer
- 4 FDM – How it Works
- 5 Structure of an FDM 3D Printer
- 6 Resin 3D Printing – How it Works
- 7 Structure of a Resin 3D Printer
- 8 First Steps with a 3D Printer
- 9 3D Printing Materials for Beginners
- 10 Simple 3D Models to Start With
- 11 The Right Software to get Started
- 12 Troubleshooting in 3D Printing
- 13 FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing is an area with a high degree of design freedom and efficient use of materials, which is used for both private and industrial applications with different processes such as FDM and SLA.
- When buying a 3D printer, private users should compare filament and resin printers, with FDM being cheaper to buy but showing visible layers, while resin offers significantly higher precision but is slightly more expensive and more complicated to post-process.
- For beginners in 3D printing, it is essential to calibrate the printer carefully and start with simple models and familiarize yourself with suitable software and troubleshooting.
3D printing can be difficult – especially in the beginning. Many beginners struggle with print errors, poor print bed adhesion, or don’t know how to properly set up the slicer.
That’s why I created an online course to get everyone up to my expert level and as quickly as possible.
The course covers everything you need to know about FDM 3D printing to get perfect results every time. Click the link below to learn more about the content and what to expect (and don’t worry: there are no tests! Learn at your own pace, completely stress-free).
3D Printing Basics
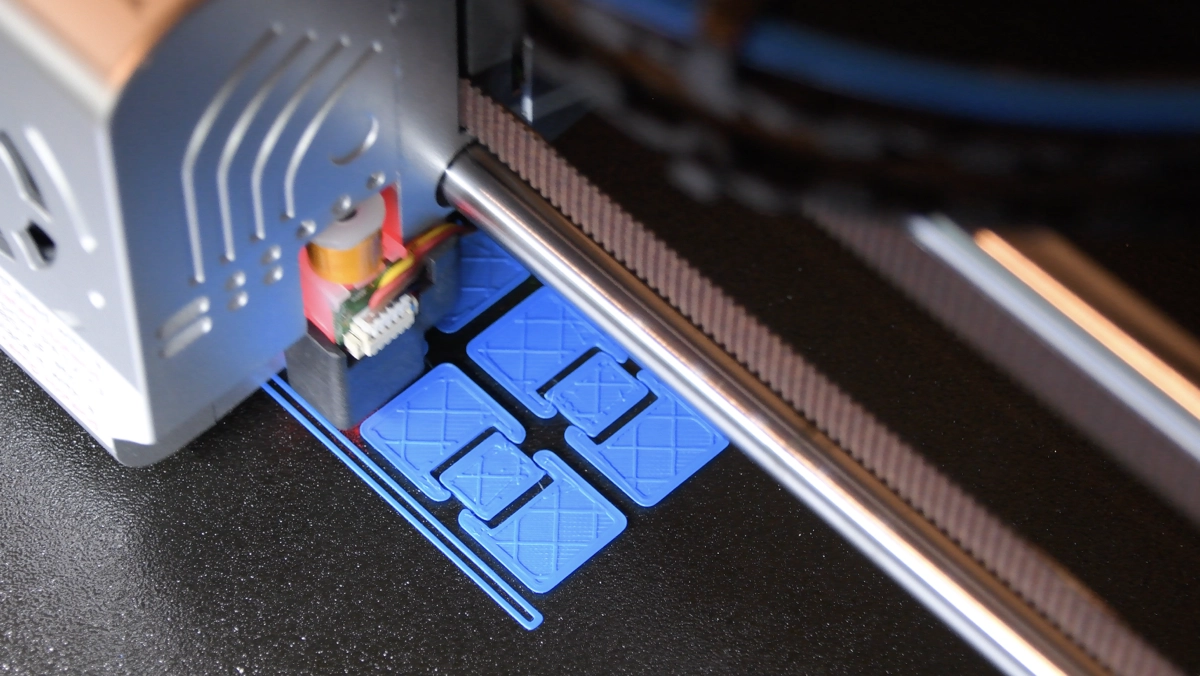
Additive manufacturing, better known as 3D printing, is a revolutionary manufacturing process in which objects are built up layer by layer. This technology enables a high degree of design freedom and the efficient use of materials.
Complex geometries and designs can thus be realized, which is particularly useful for prototypes and series production. Companies can use 3D printing to optimize their production processes and develop innovative solutions.
In the private sector, 3D printing with filament (FDM) and 3D printing with resin (SLA/DLP/LCD) are the most widespread. However, this form of additive manufacturing is also a rapidly growing field in the production industry, with an expected annual growth rate of around 20 percent over the next five years.
In addition to FDM and STL 3D printing, processes such as powder bed-based laser beam melting, binder jetting and cold gas spraying are also used in the industry.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer

There are a few factors to consider when choosing the right 3D printer for your needs. FDM printers are recommended for private use because they are:
- cost-efficient
- offer the ability to produce small parts quickly
- are easy to maintain
- use relatively inexpensive filament
However, they also have disadvantages such as visible layers on the prints.
Resin printers, on the other hand, offer excellent value for money with high precision and surface finish quality. They are particularly suitable for printing miniatures or other objects with lots of small details. However, they are pricier than FDM printers and require more complicated post-processing.
Here is a detailed comparison of the two technologies: FDM vs. SLA – Filament vs. Resin: Differences, Pros & Cons

FDM – How it Works
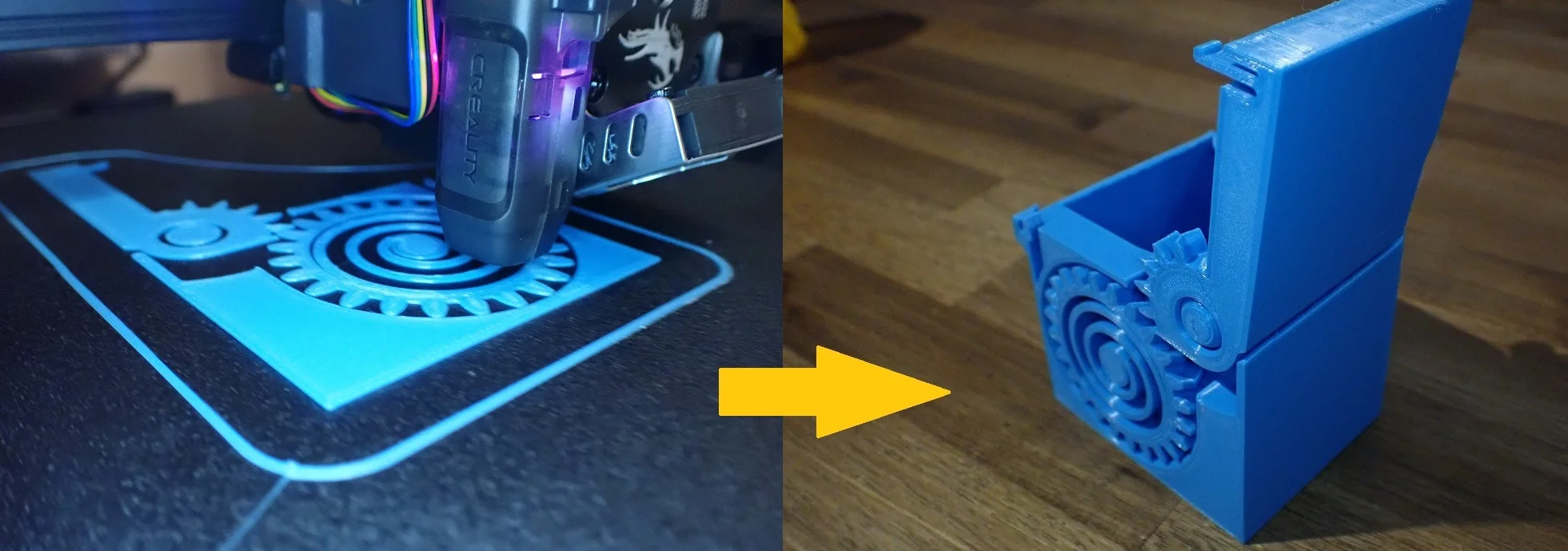
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a widely used 3D printing process. In this process, a plastic filament is pressed through a nozzle, which applies it to a preheated printing plate. The nozzle moves in predetermined paths, building up the object layer by layer.
This process is particularly popular as it is relatively inexpensive and a variety of materials are available. However, the finished prints can have visible layers, which can affect the surface quality.
Structure of an FDM 3D Printer
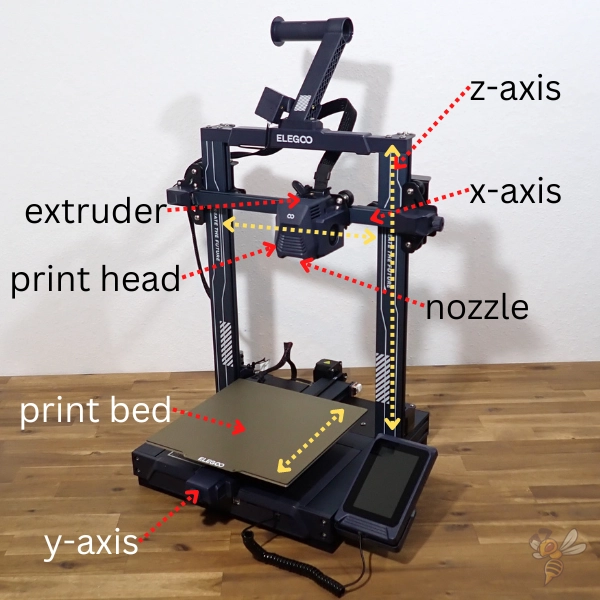

An FDM 3D printer consists of several main components. The extruder is the heart of the printer. It melts the filament and applies it to the print bed. The print bed is the platform on which the object is printed. It can be heated to ensure better adhesion of the print object.
The movement of the extruder is controlled by three axes: the X-axis moves the extruder to the left and right, the Y-axis moves the print bed forwards and backwards and the Z-axis raises and lowers the extruder (there are also other types of movement in FDM 3D printers such as Delta 3D printers). This precise control enables the printer to create complex geometric shapes.
Resin 3D Printing – How it Works
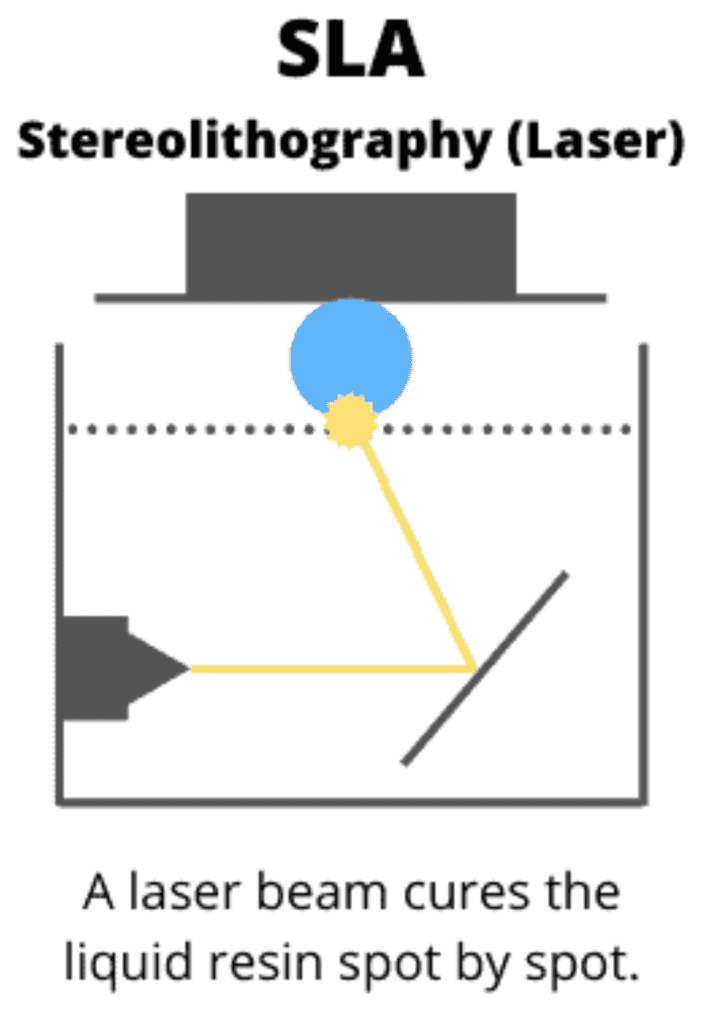
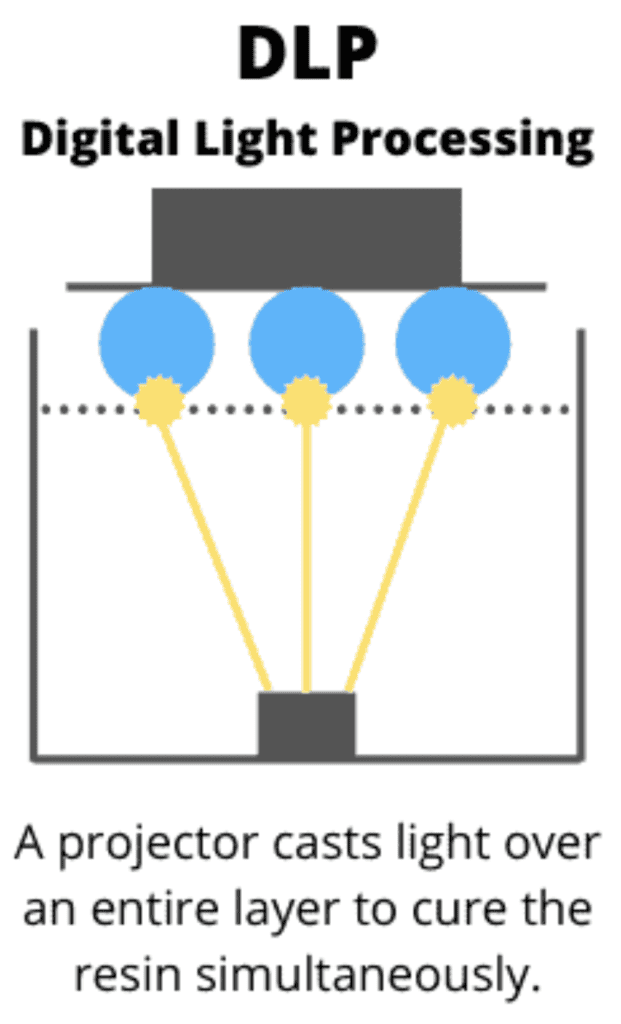
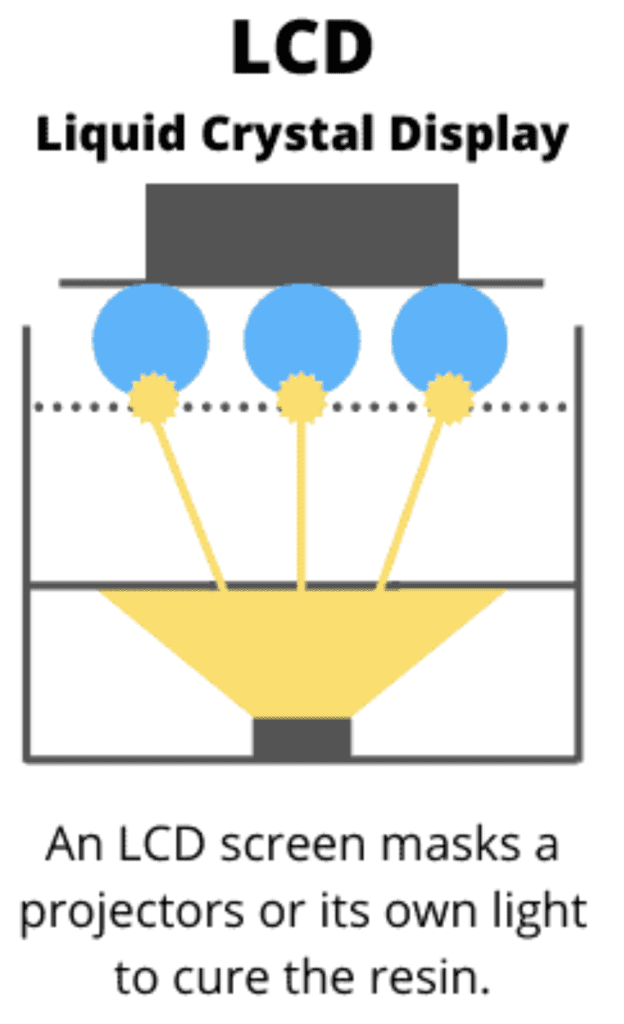
3D printing with synthetic resin is another popular 3D printing process. In this process, a light-sensitive resin is cured with UV light. The printer builds up the object layer by layer, exposing the resin in a container and thus solidifying it.
Resin printers offer very high print quality and can produce very fine details. However, they are more expensive to purchase than FDM printers and the post-processing of the printed object is more complex. An entry-level printer could be a good alternative for beginners.
Structure of a Resin 3D Printer
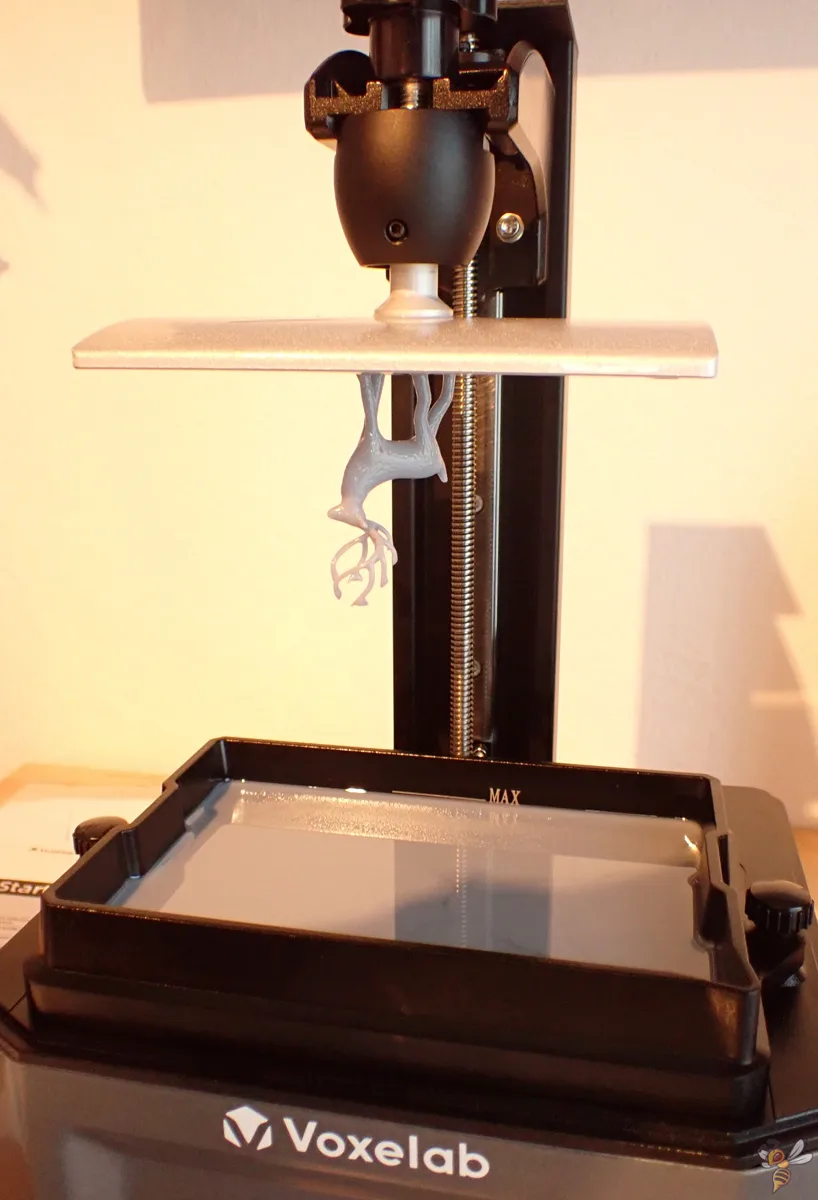


A resin 3D printer also consists of several main components. In contrast to the FDM printer, however, no filament is used here, but a liquid resin. This resin is stored in a container located underneath the printing plate.
The printing plate is immersed in the container and a UV light source exposes the resin to solidify it. The printing plate moves upwards after each layer and the next layer of resin is exposed. This creates the object from the bottom up.
First Steps with a 3D Printer

Once you have received your new 3D printer, there are a few important steps you should take before you start printing. First, you should calibrate the 3D printer. Calibration is essential for the accuracy of the prints and should be carried out carefully.
It is also important that you level the print bed correctly. An incorrectly leveled print bed can lead to printing errors and requires precise adjustment.
TIP: Learn how to calibrate your 3D printer to get perfect results every time in my 3D printing course: FDM 3D Printing: The Comprehensive Course from A to Z
(The course teaches everything you need to know for FDM 3D printing in over 60 lessons. The course will get beginners up to my level in no time!)
3D Printing Materials for Beginners


There are a variety of materials that you can use for 3D printing. For FDM printers, PLA, ABS, TPU and PETG are the most common materials. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right material depends on the application you have in mind.
FDM 3D printers process thermoplastics in a wide range of variations, colors and properties. This material is called filament and comes in diameters of 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm.
The filament is supplied on small, tightly rolled spools and hung on a filament holder on the 3D printer. The extruder unwinds the filament and pushes it to the hot end where it is melted.
The most popular filament by far is PLA (polylactic acid). It is inexpensive, easy to process, environmentally friendly and offers sufficient mechanical stability for the finished printed objects. Ideal for beginners!
Here is a list of the most important filament types:
- Standard:
- PLA
- ABS
- PETG
- Special filaments:
- Flexible: TPU
- Blends: Wood filament, metal filament
- Technical: Nylon, PC
- For support structures with dual extruder: HIPS, PVA
Each of these filaments has special properties and is easier or more difficult to process than others. Some of these filaments, such as ABS, require stable and higher ambient temperatures than other filaments. Such filaments can only be printed with 3D printers with an enclosure.
PLA filament is particularly interesting for beginners as it is easy to process and any FDM 3D printer can process this filament.
Correct storage is important for each of these filaments. The following environmental influences have a negative effect on the filament:
- Humidity: Filaments absorb moisture from the environment. This moisture escapes suddenly when heated and can lead to various printing errors.
- Sunlight: UV radiation causes filament to become brittle. A broken filament in the extruder or the cold bridge before the hot end can be very frustrating.
- Dust: Foreign bodies on the filament lead to inaccuracies in the finished model. Dust particles, lint or other foreign bodies create bubbles, holes or other defects that look unsightly on the surface.
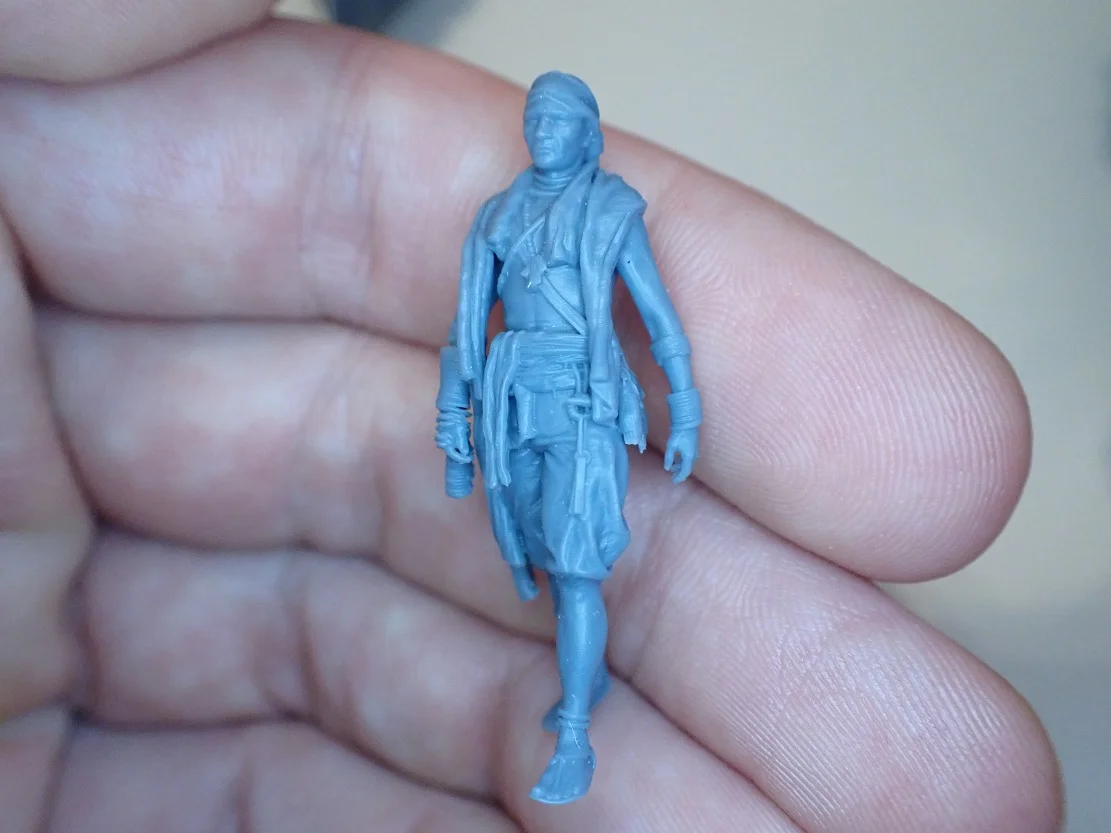
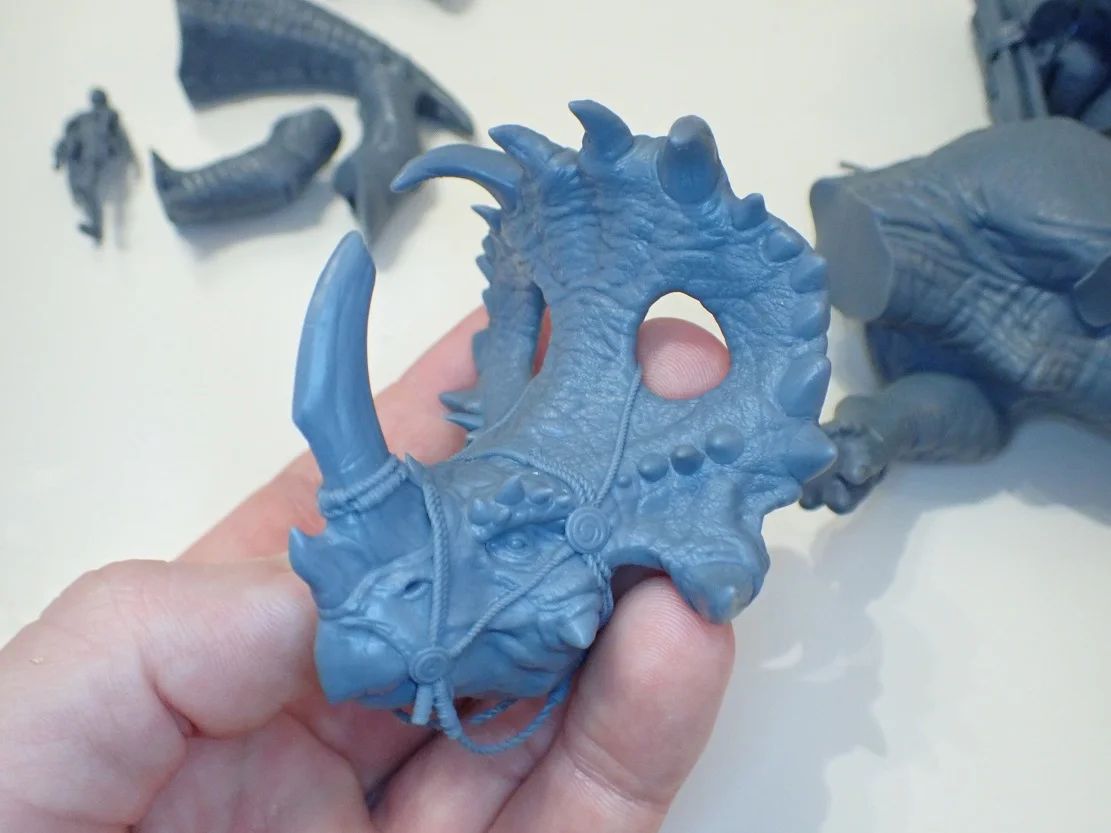
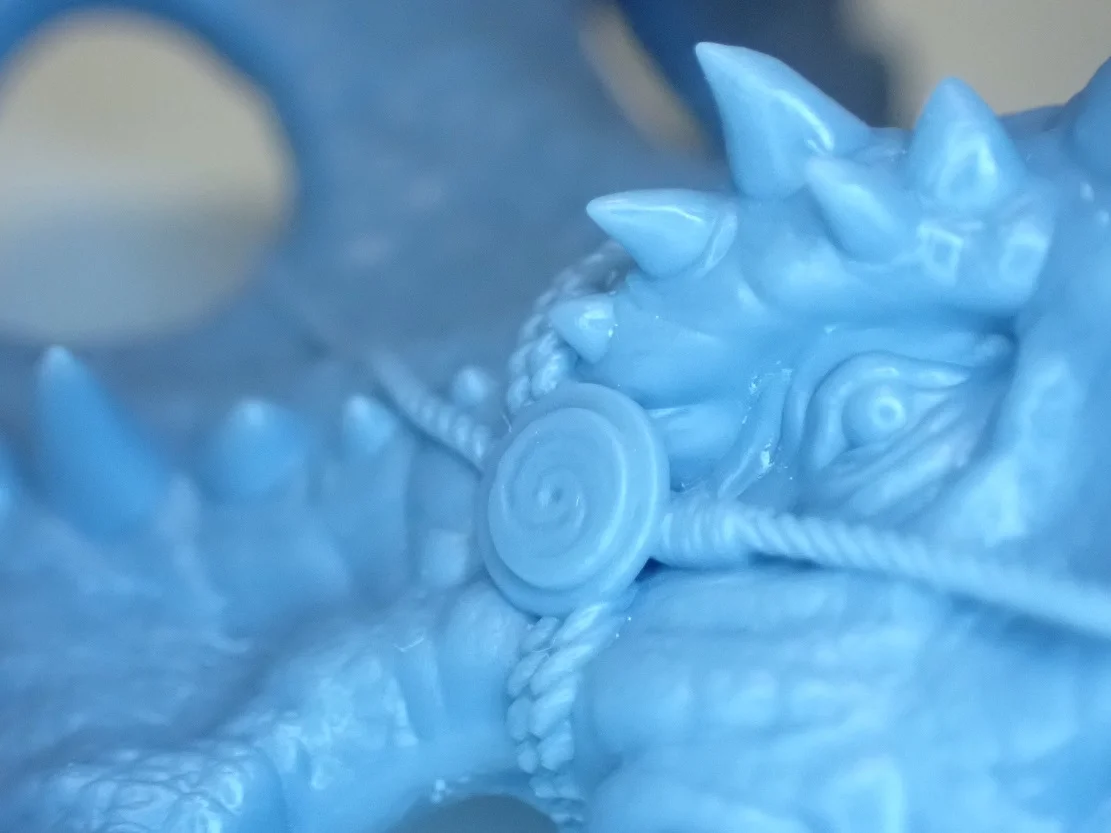




A special resin is usually used for SLA printers. Although the choice of resins is not as wide as for filaments for FDM printers, there are different types of resins with different properties and colors.
Here is a list of the most important types of resin:
- Standard Resin: These resins are usually the cheapest and can be used by most resin 3D printers. These standard resins have only medium mechanical strength and are quite brittle when cured. They are best suited for decorative objects.
- Transparent resin: Transparent resins are more difficult to cure, but offer interesting optical effects.
- Flexible resin: Flexible resin is used in technical applications for components that need to be flexible.
- Plant-based resin: Here, aggressive chemicals are not used in order to make the resin more compatible with health and the environment. The two main disadvantages are higher costs and longer curing times. I mainly use plant-based resins.
- ABS-like resin: For technical applications, objects must have higher mechanical stability. These resins have a higher hardness and elasticity than standard resins.
- Water-soluble resin: Normal synthetic resins must be washed with isopropyl alcohol. The water-soluble resins can also be dissolved with water, which makes reworking easier.
Simple 3D Models to Start With
If you are a 3D printing beginner and starting out with 3D printing, it is a good idea to start with simple projects. A simple cube is a good beginner’s project that you can use to test the function and precision of your 3D printer. The 3D-Benchy is particularly popular as a test object, as it tests various printing errors and gives a good overall picture of the accuracy of the 3D printer (link to 3D model).
There are numerous portals on the internet where you can find 3D models. These 3D print templates range from simple models for calibration to complex decorative objects.
The Right Software to get Started
To create and print 3D models, you need the right software and the right device. For beginners, we recommend Tinkercad, a simple CAD program that is ideal for getting started with 3D modeling.
There are also a number of programs that you can use to “slice” your 3D models to prepare them for printing. Cura is a popular free slicer program that is suitable for most FDM printers.
Troubleshooting in 3D Printing
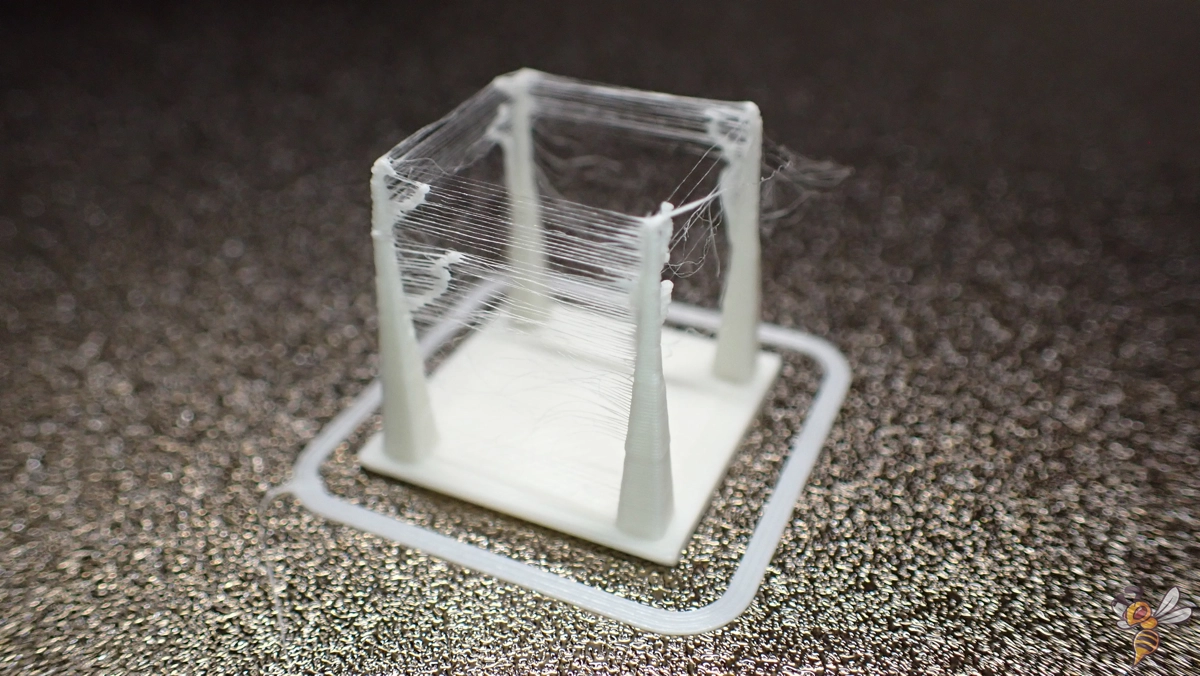

Various problems can occur during 3D printing. One of the most common problems at the beginning is stringing. To avoid this, the retraction settings of your 3D printer should be correctly calibrated. Correct leveling of the print bed is also essential to avoid many printing problems.
Here you can find a detailed guide to all printing errors you may encounter in 3D printing: 3D Printer Troubleshooting: Step-by-Step Guide with Images
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
How difficult is it to use a 3D printer?
Modern 3D printers have become very easy to use and can be easily mastered by beginners with no previous experience of the technology.
What can you do with a 3D printer?
With a 3D printer, you can not only produce decorative objects, but also print a variety of practical items for the home. The various materials available offer you countless possibilities to create individual and useful objects that are tailored to your exact needs.
How much does an entry-level 3D printer cost?
An entry-level 3D printer is available from around $200. However, to avoid frequent problems with 3D printing, you should choose a 3D printer with a slightly higher price tag. 3D printers in the price range between $350 and $450 usually offer good upgrades to avoid errors and make operation easier.
Which materials are best for 3D printing for beginners?
PLA for FDM printers and standard resin for SLA printers are the best materials for beginners to get started with 3D printing.
Disclosure: This website is the property of Martin Lütkemeyer and is operated by Martin Lütkemeyer. Martin Lütkemeyer is a member of the Amazon Services LLC and other Affiliate Programs. These are affiliate advertising programs designed to enable websites to earn advertising revenue through advertising and linking to Amazon.com and others. Links marked with * are affiliate links.


