- Wet Filament: Prevention, Symptoms & Drying - July 18, 2024
- Sovol SV08 – Best PrusaSlicer Settings & Profile - June 26, 2024
- Sovol SV08 – Best Orca Slicer Settings & Profile - June 26, 2024
Disclosure: Links marked with * are Affiliate Links. I earn from qualifying purchases if you decide to make a purchase through these links – at no additional cost for you!
It’s fun to use 3D printing to create things that not only look good but are also useful. The possibilities are almost endless.
If you use the filament PLA* for your 3D objects, the question arises whether kitchen utensils such as drinking cups or food storage boxes, which come into daily contact with food and beverages, are safe and harmless for humans.
The answer to whether PLA is food safe is Yes – as long as you consider the following:
- The object must be as smooth as possible.
- Use only PLA filaments without additives.
- Use a stainless steel nozzle.
- The nozzle must be completely clean.
- PLA is not suitable for the dishwasher.
- Coating with food-safe epoxy resin for frequent use.
The following text provides you with a wealth of interesting information about PLA printing material and is intended to answer the question in detail as to whether the use of polylactic acid for 3D printing of kitchen utensils can be considered safe. You will also find useful information on the biodegradability of PLA.

Table of Contents:
PLA Consists of Biological Materials
PLA or polylactic acid is a bioplastic printing material, which is obtained from natural materials such as corn, tapioca or potatoes. Lactic acid is also an organic acid that plays an important role in our daily life. The sore muscles you experience after a too extended sports session and the taste of sour milk are some well-known examples of the role of lactic acid.
Everything that contains glucose can be converted into lactic acid. Since corn is considered the preferred source of glucose, it is also increasingly used to obtain the PLA print material. So at first, it may seem logical to you that PLA must be considered safe since it also comes from things that are consumed regularly.
But is that really the case? Is PLA food safe?
What Does Food-Safe Mean?
First of all, it is important that you know the definition of some basic terms:
Food Quality
Food quality is not described as a single product property, it represents the totality of the characteristic properties of a product.
With regard to food, this includes in particular its harmlessness to health, since it serves our everyday nutrition.
Surfaces
Food contact surfaces include all those surfaces that are made of non-toxic materials and are designed to withstand the environment of their intended use.
This also includes the effect of cleaning agents or disinfectants as well as various cleaning processes.
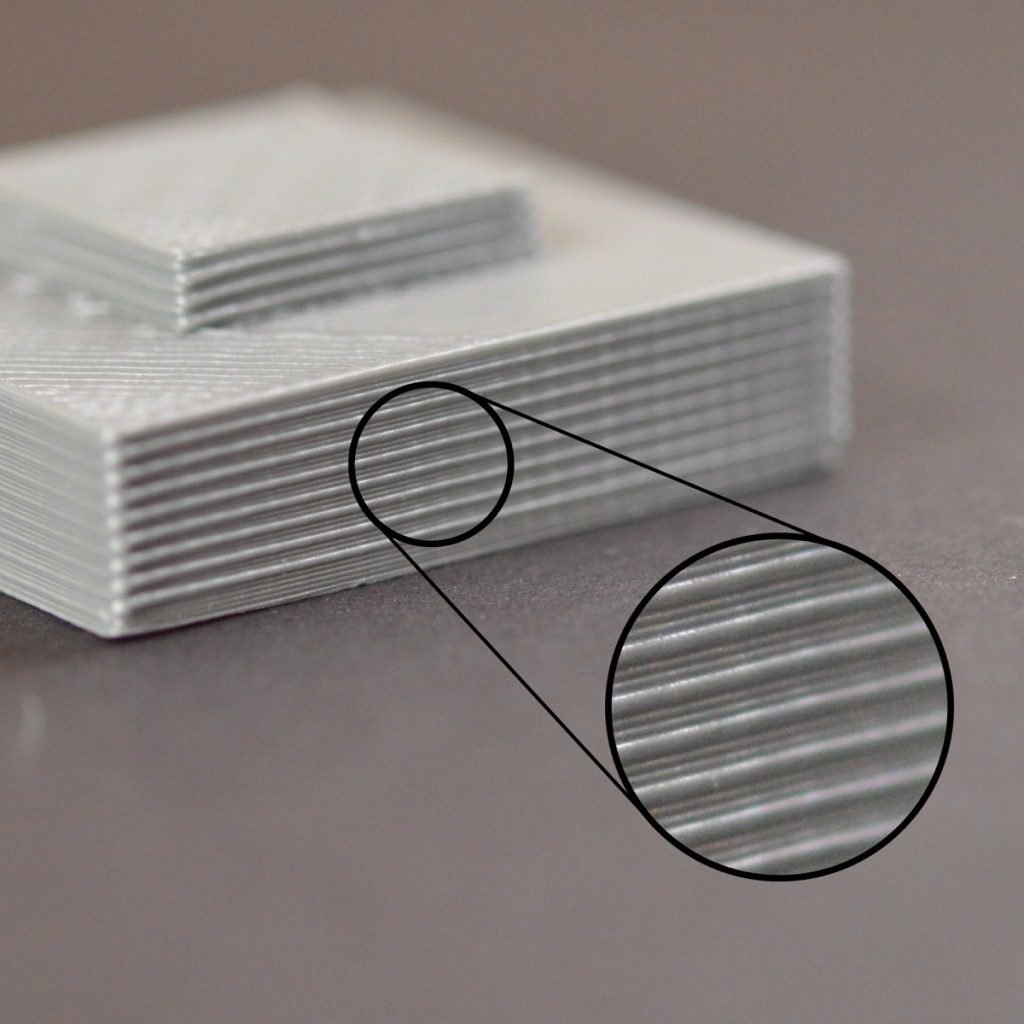
The classification of food and food safety takes into account a certain type of intake of parts, which is called migration. Particles of only a few nanometers and up to several hundred nanometers can be transferred each time different materials touch each other. This refers, for example, to the contact of components of the 3D printer with the 3D printed object and the 3D object with the food.
Since the migration rates are very low with occasional contact, the classification of food generally concerns objects that are in contact with food over a long period of time, such as containers, straws, utensils, plates and food forms.
Food-Safe
A material is considered food safe if it can be used in direct contact with food without health concerns. The smell and taste of the respective food must not be affected by the material.
To be officially classified as food safe, a material must meet the following requirements:
- There is no migration of harmful substances in direct contact with the material.
- The material does not transmit colors, odors or tastes.
- The material is safe under normal conditions of use.
- The material is durable, corrosion resistant and non-absorbent.
- The quality of the material is sufficient to withstand repeated washing.
- The material has a smooth, easy-to-clean surface without cracks and sharp internal angles.
- The material is resistant to pitting, chipping, hairline cracks, scratches, scoring, distortion and decomposition.
Why is Food Safety so Important in 3D Printing?
Meanwhile, almost everything is 3D printable. This is true not only for impressive aerospace equipment but also for the production of ordinary kitchen utensils using a 3D printer.
However, regardless of your personal project, it is fundamentally important that the materials used are absolutely safe if contact with food is intended. This not only benefits your own health but also avoids that the quality of the food suffers and that it becomes useless.
Another example is 3D printing for medical purposes. This requires the use of biocompatible materials that are completely safe and harmless to the human body.
The careful selection of the respective material is therefore important not only for gastronomic but also for medical purposes.
3D printing is widely used in many different industries. 3D printing offers a great solution for producing both food containers and personal items with impressive design work and a personal touch.
Food Safety in 3D Printing – What are the Risks?
Growth of Bacteria
When you print a 3D object that will physically touch food, you definitely want to prevent the growth of bacteria that could potentially contaminate you or others.
To prevent the growth of bacteria, you need a smooth material. Even if the object has a smooth surface, you should still pay attention to the design.
If there is a possibility that the food gets stuck in small, sharp-edged parts or even in the layers of the object, this promotes the growth of bacteria.
Chemical Products from the Printing Process
The production of 3D printed objects requires a mixture of heat and chemicals. That’s why you should be especially careful with the technologies and materials used in 3D printing your object.
This is especially true if the finished 3D object will come into contact with food in the future. Toxic particles produced during the 3D printing process can have health effects when ingested by humans.
Chemicals Directly in the Materials
Some materials used in 3D printing also contain toxic chemicals.
This is especially true for the filament ABS*, for example, which is why it is considered particularly unsafe. ABS contains a high proportion of ultra-fine particles, which can lead to health problems when ingested by humans. You should therefore refrain from using ABS in the manufacture of kitchen utensils.
PLA Food Safety Tests
PLA has been tested in the past under various conditions to assess how safe it is to be classified in contact with food. Not only were different temperatures taken into account, but also the duration of contact between the printed material and the ingredients commonly found in food.
After completion of the tests, it was determined that PLA is generally accepted as safe when in contact with food (FDA-approved).
It has been shown that PLA releases a small amount of lactic acid into food. Lactic acid is a common food ingredient that is even found in breast milk.
However, the estimated amount of lactic acid that people ingest through PLA is about 700 times less than the lactic acid intake of breastfed infants.
Contamination During the Printing Process
However, there are still warnings that PLA can be contaminated by the hot end of 3D printers.
The strong mixture of chemicals and heat used in printing and processing PLA is harmful to health. Nozzles made of stainless steel are an exception. In general, desktop 3D printers with ABS and PLA are considered to emit a lot of ultra-fine particles.
These particles can be present on the surface of your print object. Excessive inhalation or swallowing of these ultra-fine particles can have harmful effects on your health.
While ABS is also considered particularly harmful, 3D printing with PLA should also be performed in a well-ventilated room. You should also avoid eating near your 3D printer to protect your food from particles during the printing process.
Harmful Additives in PLA
PLA is colored, which means that it also contains other additives that are responsible for optimizing both its color and strength. So if you want to print models that come into contact with food, you should only consider natural and untreated PLA as a printing material. To determine whether your PLA is untreated PLA, check the safety data sheet.
This allows you to determine the chemical properties and FDA approval of your printed material and is the easiest way to determine food safety.
Inadequate Surface Finish of 3D Printing
All objects produced by 3D printing have pores in the form of tiny gaps and cracks. These in turn provide a fertile breeding ground for germs and bacteria.
PLA-printed models are no exception. Once germs and moisture have accumulated in these pores, it is no longer possible to clean them completely. The main reason for this is that PLA is not dishwasher-safe, as it can warp or even melt under high temperatures.
These circumstances lead to the theory that PLA may only be safe for single use or for simple things like water.
Repeated use, on the other hand, is to be considered a health hazard. If your 3D prints are disposable, the formation of bacteria is usually not a problem. However, if you plan to use the cups or plates more than once, special care should be taken.
However, by sealing a printed object with a food-grade epoxy or sealant, you also have the opportunity to fill in any gaps where bacteria may accumulate. A good option for PLA filaments is polyurethane, which you can find in most hardware stores. It is also advisable not to bring the 3D printed model into contact with raw meat or eggs, which are more susceptible to harmful bacterial growth.
The fact that PLA is not dishwasher safe doesn’t mean you can’t fully wash your 3D print objects. Instead of using a dishwasher, you can wash your objects after use with lukewarm water and a mild antibacterial detergent. This reduces the risk of a molten print and removes all surface bacteria.
The main reason why PLA is often used in 3D printing of kitchenware is that it is derived from ordinary food and is biodegradable.
The Biodegradability of PLA
You are wondering how long the process of biodegradation of PLA takes and how it exactly works? Both depend heavily on the environment.
For a visible degradation of PLA within one year, the three basic elements heat, moisture and microbes are necessary.
PLA decomposes best in high-temperature environments with a large number of microorganisms. This may include a compost heap, but it should provide a temperature of 60 degrees Celsius, which is the PLA glass transition temperature.
If you put the 3D object deep into the compost heap, it will take about six months under these conditions before you can see visible cracks and signs of decay.
However, at room temperature and normal pressure, PLA takes several years to decompose. This process cannot be accelerated by sunlight. Without a corresponding heat effect, UV light merely causes the material to lose its color and become pale, just as one is used to from other plastics.
Whether this slow process of biodegradation is good or bad strongly depends on your perspective and the intended use of your 3D object. According to the principles of sustainable development, biodegradable materials are ideal because they ultimately return to nature. This is an advantage, for example, in situations where the object is supposed to disappear after a certain time, such as bone surgery.
On the other hand, most printed objects should remain unchanged, which is the case with the majority of 3D prints. As mentioned earlier, the biodegradation of PLA requires various conditions that are not present in the everyday environment. Also, if you keep your PLA prints in a cool, dry place, you have nothing to worry about.
Summary:
- PLA is biodegradable due to its natural origin. Since various microorganisms can use PLA as a food source, it is also compostable.
- For the biological decomposition of PLA, moisture, a temperature of 60 degrees Celsius and microorganisms are required, which can be found in the garden soil, for example.
- Under good conditions, PLA shows signs of biodegradation after six months.
- Under normal room conditions, PLA lasts many hundreds of years.
Related Questions
What other food grade materials can be used in 3D printing?
There are other print materials that can be used in 3D printing to create objects that will come into contact with food in the future.
Ceramics have proven to be particularly suitable for this purpose, as they can be used to create food-safe and additionally resistant objects using 3D printing. Cups, plates or even saucers can be 3D printed with ceramics without the use of toxic chemicals.
Polyethylene terephthalate or the PET filament* is also suitable. Polyethylene terephthalate is a common material for the production of plastic bottles or other classic food containers.
It is known that it is absolutely food safe. One of the main advantages of this material is that it can be completely recycled, often on an industrial scale.
Can the 3D printer also print food?
3D printers capable of printing food are also known as food printers.
They use various foods instead of ink like an inkjet printer or plastic like a traditional 3D printer to produce an edible end product.
Food printers are currently under development by NASA, which has been a major driver of general 3D printing. In the past, a so-called 3D pizza printer successfully created a pizza and even baked it.
Further variations of food printers are currently the chocolate printer and the pancake printer.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, the question of whether a kitchen utensil produced using 3D printing is food safe cannot be clearly answered in the affirmative or negative. If you choose to use your 3D printed objects for food applications, you must carefully consider the risks associated with each individual use.
Objects such as knives and cookie cutters do not come into contact with food or the mouth for long periods of time so that they should be safe in terms of food quality even without filament.
However, if you want to print a coffee mug or a food container, you should take additional precautions.
This article is only intended to help you with your research – we don’t want you to get sick from improper use of 3D printed objects!
Disclosure: This website is the property of Martin Lütkemeyer and is operated by Martin Lütkemeyer. Martin Lütkemeyer is a member of the Amazon Services LLC and other Affiliate Programs. These are affiliate advertising programs designed to enable websites to earn advertising revenue through advertising and linking to Amazon.com and others. Links marked with * are affiliate links.

